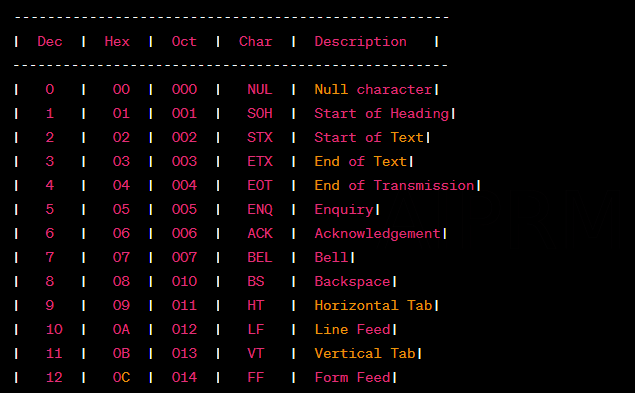
An ASCII table is a reference guide that maps decimal, hexadecimal, and octal values to their corresponding characters in the ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) character set.
ASCII is a widely used character encoding standard that assigns unique numeric codes to represent various characters, like Decimal to Ascii including letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and control characters.
The ASCII table provides a comprehensive overview of these codes, allowing users to easily identify and understand the characters associated with specific numerical values.
ASCII Table of Characters Codes and Symbols
| Dec | Hex | Oct | Char | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 00 | 000 | NUL | Null character |
| 1 | 01 | 001 | SOH | Start of Heading |
| 2 | 02 | 002 | STX | Start of Text |
| 3 | 03 | 003 | ETX | End of Text |
| 4 | 04 | 004 | EOT | End of Transmission |
| 5 | 05 | 005 | ENQ | Enquiry |
| 6 | 06 | 006 | ACK | Acknowledgement |
| 7 | 07 | 007 | BEL | Bell |
| 8 | 08 | 010 | BS | Backspace |
| 9 | 09 | 011 | HT | Horizontal Tab |
| 10 | 0A | 012 | LF | Line Feed |
| 11 | 0B | 013 | VT | Vertical Tab |
| 12 | 0C | 014 | FF | Form Feed |
| 13 | 0D | 015 | CR | Carriage Return |
| 14 | 0E | 016 | SO | Shift Out |
| 15 | 0F | 017 | SI | Shift In |
| 16 | 10 | 020 | DLE | Data Link Escape |
| 17 | 11 | 021 | DC1 | Device Control 1 |
| 18 | 12 | 022 | DC2 | Device Control 2 |
| 19 | 13 | 023 | DC3 | Device Control 3 |
| 20 | 14 | 024 | DC4 | Device Control 4 |
| 21 | 15 | 025 | NAK | Negative Acknowledgment |
| 22 | 16 | 026 | SYN | Synchronous Idle |
| 23 | 17 | 027 | ETB | End of Transmission Block |
| 24 | 18 | 030 | CAN | Cancel |
| 25 | 19 | 031 | EM | End of Medium |
| 26 | 1A | 032 | SUB | Substitute |
| 27 | 1B | 033 | ESC | Escape |
| 28 | 1C | 034 | FS | File Separator |
| 29 | 1D | 035 | GS | Group Separator |
| 30 | 1E | 036 | RS | Record Separator |
| 31 | 1F | 037 | US | Unit Separator |
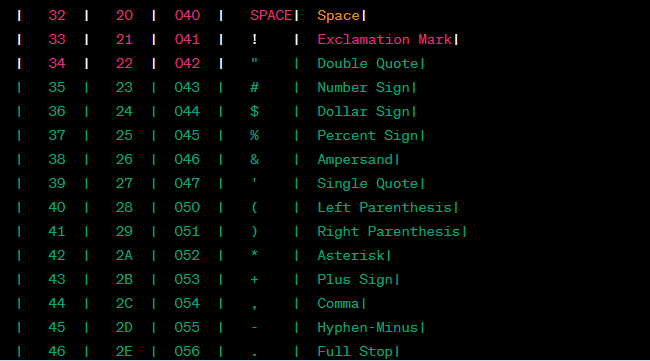
| 32 | 20 | 040 | SPACE | Space |
| 33 | 21 | 041 | ! | Exclamation Mark |
| 34 | 22 | 042 | “ | Double Quote |
| 35 | 23 | 043 | # | Number Sign |
| 36 | 24 | 044 | $ | Dollar Sign |
| 37 | 25 | 045 | % | Percent Sign |
| 38 | 26 | 046 | & | Ampersand |
| 39 | 27 | 047 | ‘ | Single Quote |
| 40 | 28 | 050 | ( | Left Parenthesis |
| 41 | 29 | 051 | ) | Right Parenthesis |
| 42 | 2A | 052 | * | Asterisk |
| 43 | 2B | 053 | + | Plus Sign |
| 44 | 2C | 054 | , | Comma |
| 45 | 2D | 055 | – | Hyphen-Minus |
| 46 | 2E | 056 | . | Full Stop |
| 47 | 2F | 057 | / | Slash |
| 48 | 30 | 060 | 0 | Digit Zero |
| 49 | 31 | 061 | 1 | Digit One |
| 50 | 32 | 062 | 2 | Digit Two |
| 51 | 33 | 063 | 3 | Digit Three |
| 52 | 34 | 064 | 4 | Digit Four |
| 53 | 35 | 065 | 5 | Digit Five |
| 54 | 36 | 066 | 6 | Digit Six |
| 55 | 37 | 067 | 7 | Digit Seven |
| 56 | 38 | 070 | 8 | Digit Eight |
| 57 | 39</“`html | 071 | 9 | Digit Nine |
| 58 | 3A | 072 | : | Colon |
| 59 | 3B | 073 | ; | Semicolon |
| 60 | 3C | 074 | < | Less-Than Sign |
| 61 | 3D | 075 | = | Equals Sign |
| 62 | 3E | 076 | > | Greater-Than Sign |
| 63 | 3F | 077 | ? | Question Mark |
| 64 | 40 | 100 | @ | At Sign |
| 65 | 41 | 101 | A | Uppercase A |
| 66 | 42 | 102 | B | Uppercase B |
| 67 | 43 | 103 | C | Uppercase C |
| 68 | 44 | 104 | D | Uppercase D |
| 69 | 45 | 105 | E | Uppercase E |
| 70 | 46 | 106 | F | Uppercase F |
| 71 | 47 | 107 | G | Uppercase G |
| 72 | 48 | 110 | H | Uppercase H |
| 73 | 49 | 111 | I | Uppercase I |
| 74 | 4A | 112 | J | Uppercase J |
| 75 | 4B | 113 | K | Uppercase K |
| 76 | 4C | 114 | L | Uppercase L |
| 77 | 4D | 115 | M | Uppercase M |
| 78 | 4E | 116 | N | Uppercase N |
| 79 | 4F | 117 | O | Uppercase O |
| 80 | 50 | 120 | P | Uppercase P |
| 81 | 51 | 121 | Q | Uppercase Q |
| 82 | 52 | 122 | R | Uppercase R |
| 83 | 53 | 123 | S | Uppercase S |
| 84 | 54 | 124 | T | Uppercase T |
| 85 | 55 | 125 | U | Uppercase U |
| 86 | 56 | 126 | V | Uppercase V |
| 87 | 57 | 127 | 127 | DEL |
| 58 | 3A | 072 | : | Colon |
| 59 | 3B | 073 | ; | Semicolon |
| 60 | 3C | 074 | < | Less-Than Sign |
| 61 | 3D | 075 | = | Equals Sign |
| 62 | 3E | 076 | > | Greater-Than Sign |
| 63 | 3F | 077 | ? | Question Mark |
| 64 | 40 | 100 | @ | At Sign |
| 65 | 41 | 101 | A | Uppercase A |
| 66 | 42 | 102 | B | Uppercase B |
| 67 | 43 | 103 | C | Uppercase C |
| 68 | 44 | 104 | D | Uppercase D |
| 69 | 45 | 105 | E | Uppercase E |
| 70 | 46 | 106 | F | Uppercase F |
| 71 | 47 | 107 | G | Uppercase G |
| 72 | 48 | 110 | H | Uppercase H |
| 73 | 49 | 111 | I | Uppercase I |
| 74 | 4A | 112 | J | Uppercase J |
| 75 | 4B | 113 | K | Uppercase K |
| 76 | 4C | 114 | L | Uppercase L |
| 77 | 4D | 115 | M | Uppercase M |
| 78 | 4E | 116 | N | Uppercase N |
| 79 | 4F | 117 | O | Uppercase O |
| 80 | 50 | 120 | P | Uppercase P |
| 81 | 51 | 121 | Q | Uppercase Q |
| 82 | 52 | 122 | R | Uppercase R |
| 83 | 53 | 123 | S | Uppercase S |
| 84 | 54 | 124 | T | Uppercase T |
| 85 | 55 | 125 | U | Uppercase U |
| 86 | 56 | 126 | V | Uppercase V |
| 87 | 57 | 127 | W | Uppercase W |
| 88 | 58 | 130 | X | Uppercase X |
| 89 | 59 | 131 | Y | Uppercase Y |
| 90 | 5A | 132 | Z | Uppercase Z |
| 91 | 5B | 133 | [ | Left Square Bracket |
| 92 | 5C | 134 | \ | Backslash |
| 93 | 5D | 135 | ] | Right Square Bracket |
| 94 | 5E | 136 | ^ | Caret |
| 95 | 5F | 137 | _ | Underscore |
| 96 | 60 | 140 | ` | Grave Accent |
| 97 | 61 | 141 | a | Lowercase a |
| 98 | 62 | 142 | b | Lowercase b |
| 99 | 63 | 143 | c | Lowercase c |
| 100 | 64 | 144 | d | Lowercase d |
| 101 | 65 | 145 | e | Lowercase e |
| 102 | 66 | 146 | f | Lowercase f |
| 103 | 67 | 147 | g | Lowercase g |
| 104 | 68 | 150 | h | Lowercase h |
| 105 | 69 | 151 | i | Lowercase i |
| 106 | 6A | 152 | j | Lowercase j |
| 107 | 6B | 153 | k | Lowercase k |
| 108 | 6C | 154 | l | Lowercase l |
| 109 | 6D | 155 | m | Lowercase m |
| 110 | 6E | 156 | n | Lowercase n |
| 111 | 6F | 157 | o | Lowercase o |
| 112 | 70 | 160 | p | Lowercase p |
| 113 | 71 | 161 | q | Lowercase q |
| 114 | 72 | 162 | r | Lowercase r |
| 115 | 73 | 163 | s | Lowercase s |
| 116 | 74 | 164 | t | Lowercase t |
| 117 | 75 | 165 | u | Lowercase u |
| 118 | 76 | 166 | v | Lowercase v |
| 119 | 77 | 167 | w | Lowercase w |
| 120 | 78 | 170 | x | Lowercase x |
| 121 | 79 | 171 | y | Lowercase y |
| 122 | 7A | 172 | z | Lowercase z |
| 123 | 7B | 173 | { | Left Curly Brace |
| 124 | 7C | 174 | | | Vertical Line |
| 125 | 7D | 175 | } | Right Curly Brace |
| 126 | 7E | 176 | ~ | Tilde |
| 127 | 7F | 177 | DEL | Delete |
Download Ascii Table PDF
Frequently asked Questions related to ASCII Tables:
What is the purpose of an ASCII table?
An ASCII table serves as a visual representation of the ASCII character set, enabling users to find the character associated with a particular numeric code and vice versa. It is widely used in programming, data processing, and telecommunications to facilitate the accurate representation and transmission of textual data.
How do I read an ASCII table?
An ASCII table consists of columns that display the decimal, hexadecimal, and octal values, along with the corresponding characters and their descriptions. To read the table, locate the desired value or character in its respective column to find the associated information.
Let’s say you want to find the ASCII code for the uppercase letter ‘A’. To do this, you can refer to an ASCII table.
Here are the steps to follow:
- Locate the ‘A’ row: In the ASCII table, look for the row that represents the uppercase letter ‘A’. In most ASCII tables, the uppercase letters are listed in consecutive rows.
- Identify the decimal value: In the ‘A’ row, find the column that corresponds to the decimal values. In this case, it is usually the second column. Check the value in that column, and you’ll find that the decimal value for ‘A’ is 65.
- Note the hexadecimal and octal values: Adjacent to the decimal value, you’ll find the hexadecimal and octal values. For ‘A’, the hexadecimal value is 41, and the octal value is 101.
- Understand the character description: Finally, in the ‘Char’ or ‘Character’ column, you’ll find the character associated with the decimal value. In this case, the character description for 65 is ‘A’, indicating that it represents the uppercase letter ‘A’.
By following these steps, you can read an ASCII table and find the decimal, hexadecimal, and octal values for specific characters. This example can be useful when working with ASCII-based systems, encoding or decoding text, or understanding the numeric representation of characters in programming or data processing tasks.
What is the significance of the ASCII character set?
The ASCII character set was developed to standardize character encoding across different computer systems and ensure compatibility in exchanging textual data. By assigning unique codes to characters, ASCII allows computers to accurately represent and interpret written information, enabling seamless communication and data processing.
Are there any limitations to ASCII?
ASCII originally supported only a limited range of characters, primarily consisting of the English alphabet, numbers, and common symbols. It does not include characters from other languages or special characters used in advanced formatting. As a result, extended character sets like Unicode have been developed to overcome these limitations and support a broader range of languages and symbols.
How can I use an ASCII table in programming?
In programming, an ASCII table is valuable for tasks such as converting between characters and their corresponding numeric codes, manipulating and analyzing textual data, and ensuring proper encoding and decoding of information. It provides a quick reference for programmers working with ASCII-based systems or when dealing with character manipulation in their code.
James is a software engineer and founder of the website “Decimal to ASCII”. He has a passion for technology and programming and has been in the industry for over a decade. With a strong focus on user experience and efficiency, “Decimal to ASCII” is a reliable and user-friendly tool for converting decimal to ASCII codes.